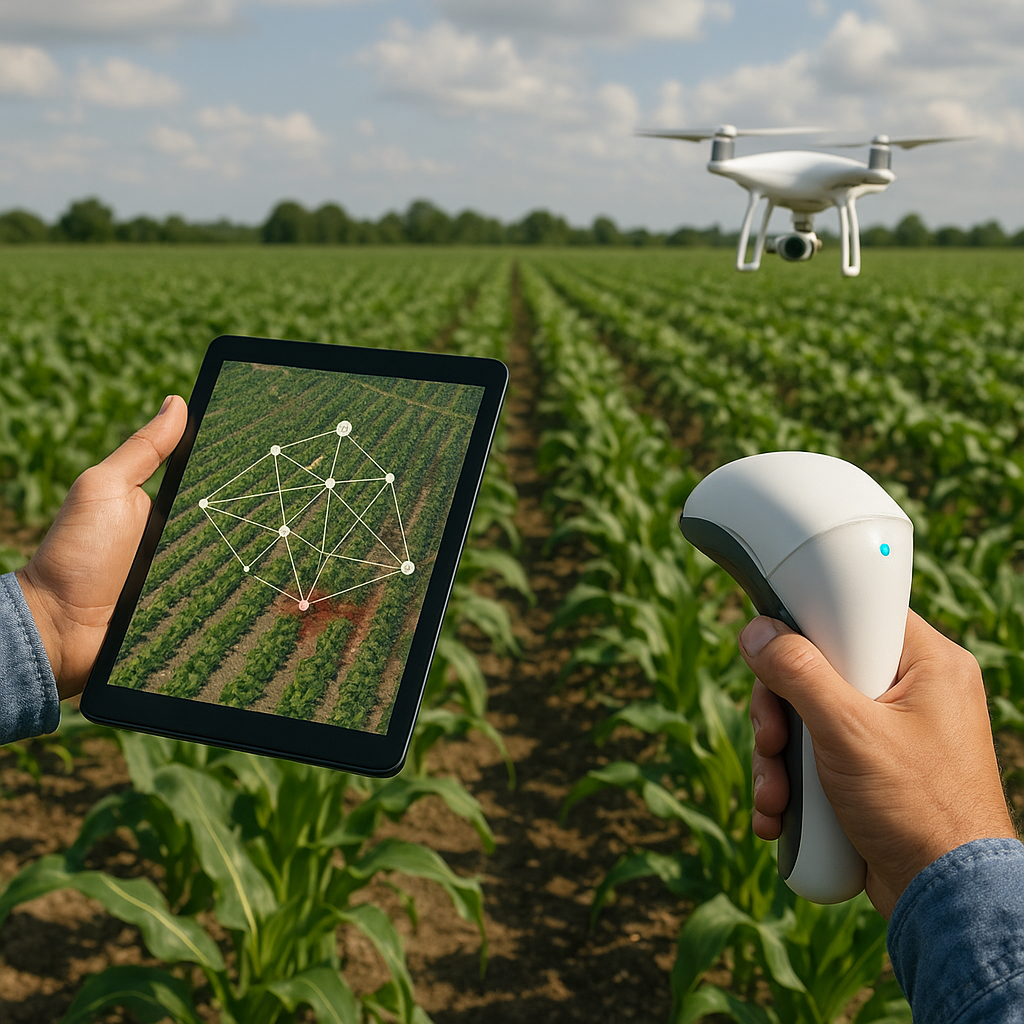
In recent years, the integration of drones into agriculture has revolutionized the way farmers monitor and manage their crops. This innovative technology offers a bird’s-eye view of fields, providing critical data that can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and promote sustainable farming practices.
The Role of Drones in Modern Agriculture
Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have become an indispensable tool in modern agriculture. Equipped with advanced sensors and cameras, these flying devices can capture high-resolution images and videos of vast agricultural landscapes. This aerial perspective allows farmers to monitor crop health, assess soil conditions, and detect pest infestations with unprecedented accuracy.
Precision Agriculture
One of the most significant contributions of drones to agriculture is the advancement of precision agriculture. This approach involves the use of technology to optimize field-level management regarding crop farming. Drones play a crucial role in this by providing detailed maps and data that help farmers make informed decisions. For instance, multispectral sensors on drones can capture images in different wavelengths, revealing variations in plant health that are not visible to the naked eye. This information enables farmers to apply fertilizers, pesticides, and water more efficiently, targeting specific areas that need attention and reducing waste.
Crop Monitoring and Health Assessment
Regular monitoring of crops is essential for maintaining their health and maximizing yield. Drones can cover large areas quickly, capturing images that can be analyzed to identify issues such as nutrient deficiencies, disease outbreaks, and water stress. By detecting these problems early, farmers can take corrective actions before they escalate, ensuring healthier crops and higher productivity. Additionally, drones can be programmed to follow specific flight paths, allowing for consistent and repeatable monitoring over time.
Benefits and Challenges of Using Drones in Agriculture
While the use of drones in agriculture offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges that need to be addressed. Understanding both the advantages and the obstacles is crucial for the successful integration of this technology into farming practices.
Benefits
- Increased Efficiency: Drones can cover large areas in a short amount of time, providing real-time data that helps farmers make quick and informed decisions.
- Cost Savings: By enabling precise application of inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides, drones help reduce waste and lower overall costs.
- Improved Crop Health: Early detection of issues allows for timely interventions, leading to healthier crops and higher yields.
- Environmental Sustainability: Precision agriculture practices supported by drone technology promote sustainable farming by minimizing the use of chemicals and conserving resources.
Challenges
- Regulatory Hurdles: The use of drones is subject to regulations that vary by country and region. Farmers must navigate these rules to ensure compliance.
- Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing and maintaining drones, as well as training personnel to operate them, can be a significant barrier for some farmers.
- Data Management: The vast amount of data generated by drones requires effective management and analysis tools to be useful. Farmers need access to software and expertise to interpret this data.
- Technical Issues: Drones are susceptible to technical problems such as battery life limitations, weather conditions, and potential malfunctions, which can impact their reliability.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Drones in Agriculture
Several case studies highlight the successful implementation of drones in agriculture, demonstrating their potential to transform farming practices.
Case Study 1: Vineyard Management in California
In California, a vineyard owner integrated drones into their management practices to monitor grapevine health and optimize irrigation. By using drones equipped with multispectral sensors, the vineyard was able to identify areas experiencing water stress and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly. This led to a significant reduction in water usage and improved grape quality, ultimately increasing the vineyard’s profitability.
Case Study 2: Rice Farming in Japan
In Japan, rice farmers have adopted drone technology to enhance crop management. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and thermal sensors are used to monitor rice paddies for signs of disease and pest infestations. The data collected allows farmers to apply targeted treatments, reducing the use of pesticides and promoting healthier crops. This approach has resulted in higher yields and better-quality rice, benefiting both farmers and consumers.
The Future of Drones in Agriculture
The future of drones in agriculture looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing adoption by farmers worldwide. As drones become more affordable and user-friendly, their use is expected to become more widespread, further revolutionizing the agricultural industry.
Integration with Other Technologies
The integration of drones with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), holds great potential for enhancing their capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze drone-collected data to provide actionable insights, while IoT devices can enable real-time monitoring and control of agricultural operations. This synergy of technologies will enable even more precise and efficient farming practices.
Policy and Regulation
As the use of drones in agriculture continues to grow, it is essential for policymakers to develop clear and supportive regulations that facilitate their adoption while ensuring safety and privacy. Collaborative efforts between governments, industry stakeholders, and farmers will be crucial in creating a regulatory framework that balances innovation with responsible use.
Education and Training
To fully realize the benefits of drones in agriculture, it is important to invest in education and training for farmers. Providing access to resources and training programs will empower farmers to effectively use drone technology and interpret the data collected. This knowledge transfer will be key to maximizing the impact of drones on agricultural productivity and sustainability.
In conclusion, drones have the potential to significantly transform agriculture by providing valuable insights and enabling more precise and efficient farming practices. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits of using drones in agriculture are substantial, offering a promising future for farmers and the agricultural industry as a whole.