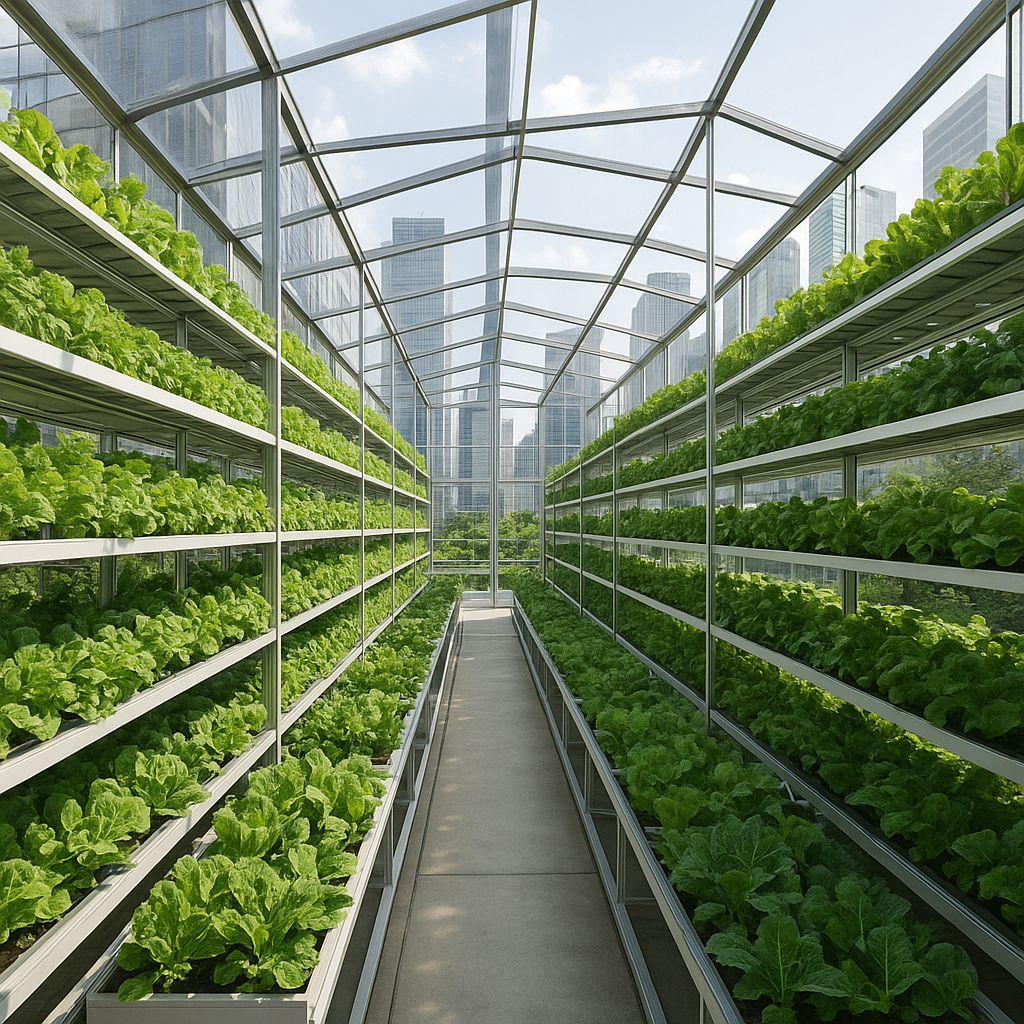
The transformation of urban landscapes through vertical farming represents a significant leap in modern agriculture. By stacking layers of crops in controlled environments, cities can cultivate fresh produce year-round, reduce transportation emissions, and optimize resource efficiency. As metropolitan populations grow, this innovative approach addresses the dual challenge of feeding millions while preserving natural ecosystems. From skyscraper greenhouses to repurposed shipping containers, vertical farming embodies a new era of urban agriculture that leverages technology, creativity, and sustainability to reinvent the way we grow food.
Emerging Technologies Driving Urban Vertical Farming
Technological breakthroughs are at the heart of the vertical farming revolution. A fusion of innovation in lighting, water management, and automation has led to controlled-environment agriculture systems that outperform traditional fields in yield and speed. Farmers and entrepreneurs are implementing precision solutions to monitor plant health, nutrient levels, and climate conditions at a granular level.
Hydroponics and Aeroponics
One of the most impactful techniques is hydroponics, where plants grow in nutrient-rich water without soil. Aeroponics advances this concept by misting nutrient solutions directly onto roots suspended in air. Both methods offer:
- Up to 90% less water usage compared to conventional soil-based agriculture.
- Reduced risk of soil-borne diseases and pests.
- Enhanced control over nutrient delivery, leading to faster growth cycles.
Advanced LED Lighting Systems
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have revolutionized indoor farming. Tailored light spectra can optimize photosynthesis during various plant development stages. Some notable advantages include:
- Energy consumption reduced by up to 50% relative to traditional grow lights.
- Customizable wavelengths to boost leaf, stem, or fruit production.
- Minimal heat emission, allowing closer lamp placement and denser planting.
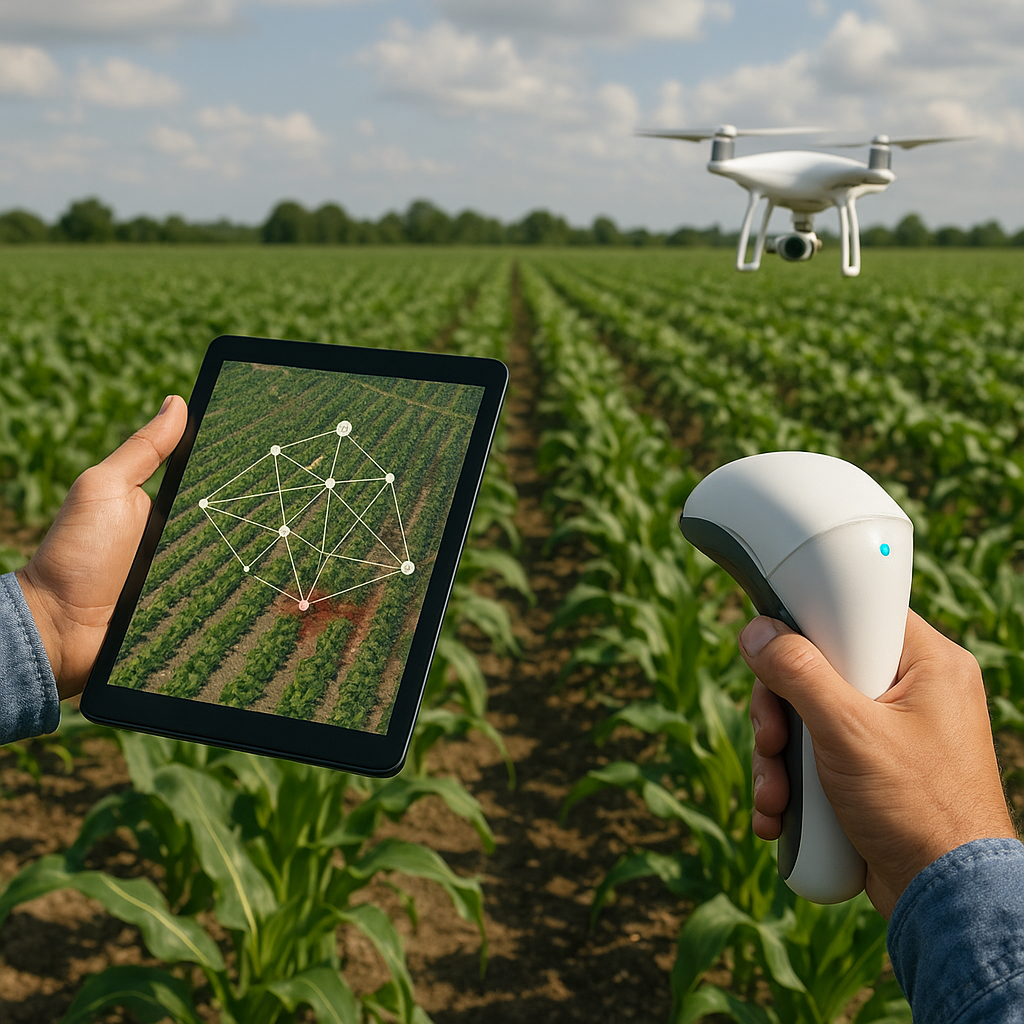
Automation and Data Analytics
Integrating Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, robotics, and artificial intelligence enables farmers to oversee vast multi-layered farms with minimal human intervention. Data-driven systems can:
- Continuously track humidity, temperature, and CO₂ levels.
- Automate nutrient dosing and pH balancing.
- Predict yield outcomes and detect early signs of plant stress.
Design and Infrastructure of Vertical Farms in Cities
Urban planners and architects are collaborating with agri-engineers to develop spaces that maximize productivity while fitting seamlessly into cityscapes. Whether retrofitting abandoned warehouses or constructing dedicated towers, the design principles remain consistent: efficient use of space, sustainability, and integration with existing infrastructure.
- Modular Construction: Prefabricated units allow scalable farm expansion and flexible layouts.
- Water Recycling: Closed-loop systems capture and reuse up to 95% of water, drastically lowering consumption.
- Climate Control: HVAC systems maintain optimal growing conditions, ensuring consistent yields regardless of external weather fluctuations.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Solar panels, wind turbines, and biogas generators offset electricity demands.
- Vertical Integration: Combining food production with retail or hospitality spaces to reduce distribution costs and offer consumers direct farm-to-table experiences.
Innovative façades featuring transparent panels and hydroponic troughs can transform office buildings into living green towers. These structures not only provide fresh produce but also improve air quality, reduce urban heat islands, and enhance city aesthetics.
Economic and Environmental Impacts
Vertical farming offers compelling economic opportunities by localizing food production, cutting down on long supply chains, and creating new job categories in agritech, maintenance, and data analysis. Initial capital expenditure can be high, but operational efficiency and shorter growth cycles lead to rapid returns on investment.
On the environmental front, vertical farms contribute to:
- Food Security: Reducing dependence on rural agriculture and mitigating supply disruptions due to weather events or transportation challenges.
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions through shorter distribution networks and energy-efficient cultivation methods.
- Protected biodiversity by lessening the need to clear farmland and reducing pesticide runoff.
- Minimized food waste, as produce can be harvested on-demand in response to real-time consumer demand.
Comparative life cycle assessments indicate that vertical farms can cut water use by over 80% and land use by more than 95% relative to conventional agriculture. With smart grid integration and renewable power, their carbon footprint continues to shrink, making them a cornerstone of sustainable cities.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite promising benefits, vertical farming must navigate several obstacles. High upfront costs for facilities and equipment pose barriers to entry. Energy consumption, while optimized, still accounts for a significant portion of operational expenses. Additionally, regulatory frameworks for novel agricultural systems often lag behind technological advancements.
Industry players are collaborating with policymakers to:
- Establish guidelines for food safety and quality standards in controlled-environment agriculture.
- Create incentives and subsidies to offset initial capital costs.
- Promote research into alternative energy sources and low-cost materials.
Looking ahead, the convergence of sustainability goals and urban development strategies will propel vertical farming into mainstream adoption. Future trends may include:
- Integration with smart city platforms for optimized resource distribution.
- Development of novel crop varieties specifically adapted to indoor environments.
- Community-driven micro-farms, enabling neighborhood-level self-reliance in fresh produce.
- Partnerships with biotechnology firms to enhance nutritional profiles and flavor through genetic and environmental optimization.
As we reimagine metropolitan food systems, vertical farming emerges as a powerful solution for feeding urban populations sustainably. The fusion of precise engineering, advanced hydroponics, and sophisticated automation heralds an agricultural paradigm shift. Embracing this dynamic model promises to reshape our skylines and plate alike, ensuring resilient and innovative food supplies for generations to come.